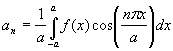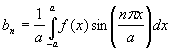
Fourier Transform WebQuest
Mathematical Introduction
Scientists and engineers are often confronted with periodic functions that are difficult to handle from the computational standpoint. In order to facilitate the analysis of these functions, they are often broken down to a sum of sinusoidal functions referred as Fourier Series.
If the function f(x) is periodic with period 2p, then its Fourier series is
Should the function have some arbitrary period 2a and be bound between –a and a then its Fourier series becomes
Even though the complete presentation of f(x) requires infinite number of terms, in practice only few terms are required to give reasonable approximation of the original function.
Coefficients
In order to find the Fourier series coefficients of a function with period 2a, the following procedure is used:
For many functions (but definitely not the majority) either the odd or even n coefficients turn out to be zero. For other functions all coefficients above some n are zero and they are represented perfectly by a finite sum of sines and cosines.
Contact me at sanguel1@ithaca.edu